A beginner’s guide to Schema markup and structured data
As a webmaster or SEO professional, you’ve probably heard about schema markup and structured data.
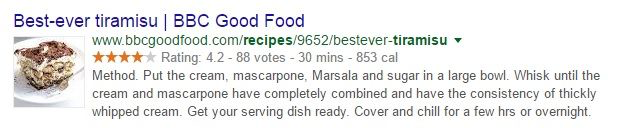
It’s not uncommon to see rich search engine results like this one:
This rich snippet is a result of structured data, which creates an enhanced description of your web page.
Structured data can have a positive impact on your web page’s search engine rankings and organic traffic. In this blog post, we’ll explore what schema and structured data is, how it is used, and what the benefits associated with it are.
What do schema markup and structured data mean?
Let’s start with the basics.
As explained earlier, schema can help you create an enhanced description of your web page. More importantly, it also helps search engines better understand the context of the page.
This is how schema.org defines the concept:
“Most webmasters are familiar with HTML tags on their pages. Usually, HTML tags tell the browser how to display the information included in the tag. For example, <h1>Avatar</h1> tells the browser to display the text string “Avatar” in a heading 1 format.
However, the HTML tag doesn’t give any information about what that text string means. “Avatar” could refer to the hugely successful 3D movie, or it could refer to a type of profile picture, and this can make it more difficult for search engines to intelligently display relevant content to a user.”
Structured data refers to the actual code you need for rich snippets. Schema refers to a library with a large collection of structured data code snippets.
Schema is used to display a variety of content, for example:
- Recipes
- Products
- Reviews
- Videos
- Music
- Event details
- Movie screening times
- Business listings
- News articles
How does structured data affect a website’s search engine rankings?
Does structured data directly affect a website’s search engine rankings and improve a web page’s position in the SERPs?
No, it does not have a direct impact. At least, there are no credible studies that indicate a direct effect of structured data on a site’s search rankings.
However, it does not mean that structured data does not have its benefits. In fact, it can have an indirect impact on a site’s search rankings.
For instance, structured data helps search engines understand the context of a web page. This allows the search engines to show your web page for relevant search queries, which increases the chances of more targeted organic traffic.
Second, structured data helps generate rich snippets, which stand out in the SERPs. A study reveals that less than 33 percent of Google’s search results have rich snippets. If your web page has one, it can potentially increase the organic click-through rate (CTR) and the number of visitors you get from search engines.
How to add structured data to your web pages
There are multiple ways of adding structured data to your web pages.
First, you can do it by manually adding the appropriate code in the HTML code of your web page, but that’s a very time-consuming, tedious, and error-prone process.
Second, you can install a WordPress plugin to simplify the process of adding structured data. Some of the plugin options are All in One Schema.org Rich Snippets and Schema Pro.
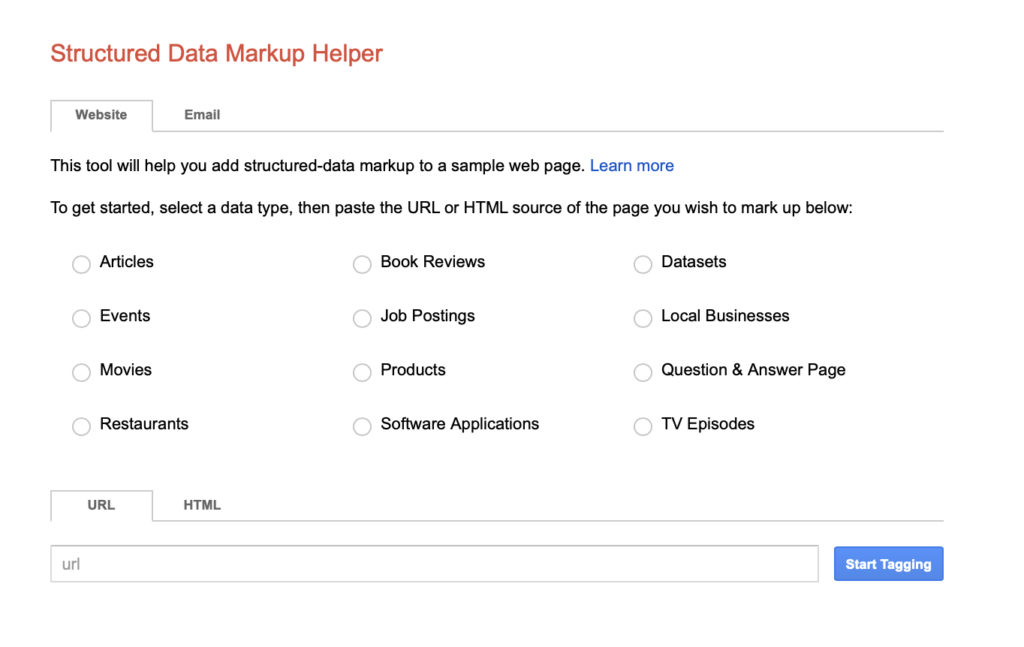
If you don’t want to install a plugin, you can also add structured data using Google’s Structure Data Markup Helper.
You will have to follow these steps:
- First, select the most appropriate category from the given options, e.g., Articles, Movies, Book Reviews, etc.
- Then paste the URL of your web page in the URL box
- Click ‘Start Tagging’
This will open your web page in a new page with a ‘My Data Items’ on the right sidebar. Depending on the category you select in the first step, you may see different options in the ‘My Data Items’ menu.
The next step requires you to highlight the section and add appropriate tags to it. For example, you can highlight the title of your page and click the ‘Name’ tag to add it as the title of the article. You can also add missing tags if you want to manually add more information.
Once all the sections are tagged appropriately, click ‘Create HTML’ to generate the web page code. You will find two output formats: JSON-LD and Microdata.
JSON-LD is the new format that Google prefers, and it is also easier to handle than Microdata.
Once you export the code in the JSON-LD output format, copy the markup code to the head section of your web page.
Testing structured data
You can also test your generated code with another Google tool: Structured Data Testing Tool.
With this information, you can tweak the structured data or add additional information that would help the search engine understand your web page more effectively and efficiently.